What is Agentic AI ?
Agentic AI is a very recent trend in the artificial intelligence. It has become very famous after the launch of ChatGPT and other generative ai models. Agentic AIs are systems that are build on deep learning on large datasets. They are characterized by reinforcement learning. Agentic AI uses foundational large language models along with contextual awareness to make it stand apart from other systems. Agentic AI works in sync across multiple agents. Meaning multiple Agents can communicate with each other and perform tasks simultaneously. Agentic AIs are smart and good at decision making because they draw there contextual awareness from large language models which are pre trained on huge corpus of data. Thus Agentic AIs can orchestrate workflows very smartly and make good decisions. These systems are autonomous in nature giving them capability to execute decision based actions just like human being do. Knowledge base and inference engines play a very important role for making Agentic AI systems smarter.
In an Agentic AI systems there are multiple agents and these agents are given with specialize tasks. These agents communicate and communicate with each other and decompose the task in order to achieve the final outcome. One of the important features of Agentic AI is their ability to use the tools based on the task given
What are AI Agents?
AI Agents existed way before generative ai was introduced to us. It was a very famous methodology pre ChatGPT era. AI Agents operated in very narrow and constrained based environment. They are rule based systems unlike the Agentic AI which draws its inference and contextual awareness from large language models. AI Agents are simpler and deployed for singular/simpler task. Complex task and context based decision making is beyond their scope. There adaptability to dynamic environment is restricted as well AI Agents can not use tools. For eg they cannot search internet, parse real time data , interact with API and tools just like how humans do.
What Are Agents in Agentic AI ?
Agents in Agentic AI systems are entity which helps share information amongst each other. There main goal is to achieve the task allocated by co ordinated decision making. In a multi agent system agents work together to achieve a common goal by collecting information and executing the tasks assigned to them. These agents are contextually aware because they are trained on Large language model. Agents learn, adapt , interact with each other and the environment, take decisions to complete the shared goals. Its similar to players in a cricket team with the sole objective to win the game.
Goal Decomposition by Agentic Ai
In an Agentic AI systems where multiple agents are interreacting with each other, the agents tackle the final outcome by divide and conquer rule. These agents decompose the task/ goals amongst themselves.
How to decompose the goals when creating Agentic Ai systems
During the creation of Agentic Ai systems we can perform the following steps
1. Goal Interpretation
- Parse a user’s instruction or system objective.
- Translate vague or abstract goals into machine-tractable targets.
-
Example: “Plan a conference” → Identify venue, speakers, agenda, logistics.
-
2. SMART Framing (if supported)
- Define the goal as Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound.
- Add constraints (resources, APIs, permissions, ethical filters).
- Set success criteria (what output or state marks completion).
3. Task Decomposition
- Break goal into sub-goals and atomic tasks.
- Use reasoning chains, recursive planning, or hierarchical models (like HTN planning – Hierarchical Task Networks).
- Validate coverage (do all subtasks together achieve the main goal?).
- Remove redundancy.
4. Dependency Mapping
- Represent subtasks as a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG).
- Identify sequential vs. parallel tasks.
- Extract the critical path (tasks that directly impact time to completion).
5. Prioritization
- Rank subtasks by scoring:
- Impact → Moves agent closer to the goal.
- Urgency → Deadlines or bottlenecks.
- Feasibility → Complexity, API cost, required data.
- Dynamic reprioritization as conditions change.
6. Execution & Feedback
- Run tasks according to the DAG + priority order.
- Monitor intermediate outputs.
- Use reflection and self-correction loops (retry, re-plan, or escalate).
- Adapt based on new constraints or failures.
7. Iterative Re-Planning
-
If a sub-goal fails or new input arrives, the agent can:
-
- Re-decompose the remaining tasks.
- Adjust the DAG.
- Continue execution.
Agentic AI task decomposition = Goal → Sub-goals → DAG → Priorities → Execution → Feedback → Adaptation.
How multi agents in Agentic AI systems communicate?
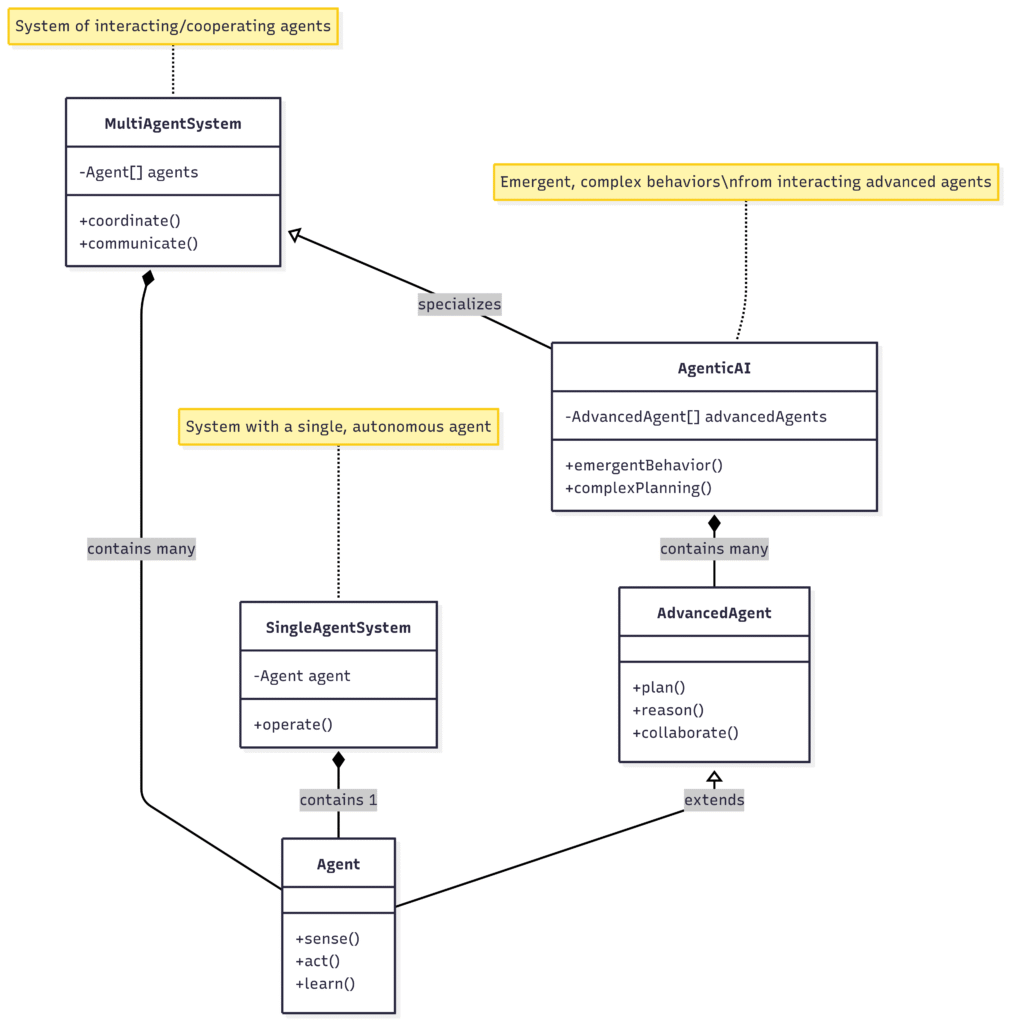
A diagram showing AI agents (single agents) vs Multi agents and its relation with Agentic AI
In a multi agent Agentic AI systems, multiple agents communicate with each other with the help of asynchronous messaging queues , shared memory buffers and also over distributed network systems. Essentially there are many ways the agents can communicate with each other. Agents in Multi Agents in Agentic AI systems can be software programmes, sensors, IOT devices etc which communicate with each other. There is smooth and efficient communication between agents , environment and organisation.
Example python code (How does multi agents work in Agentic AI systemts)
import asyncio
import random
# -------- Environment --------
class Environment:
def __init__(self):
self.tasks = asyncio.Queue() # dynamic task pool
self.events = asyncio.Queue() # messages between agents
async def broadcast(self, msg):
await self.events.put(msg)
# -------- Agents --------
class Planner:
def __init__(self, env: Environment):
self.env = env
async def run(self):
while True:
await asyncio.sleep(2)
task_id = f"T{random.randint(100,999)}"
task = {"id": task_id, "type": "work", "data": random.randint(1,5)}
await self.env.tasks.put(task)
await self.env.broadcast(f"[Planner] New task created: {task_id}")
class Worker:
def __init__(self, env: Environment, name="Worker"):
self.env = env
self.name = name
async def run(self):
while True:
task = await self.env.tasks.get()
await self.env.broadcast(f"[{self.name}] picked {task['id']}")
await asyncio.sleep(task["data"]) # simulate processing time
outcome = "success" if random.random()>0.2 else "fail"
await self.env.broadcast(f"[{self.name}] finished {task['id']} -> {outcome}")
class Monitor:
def __init__(self, env: Environment):
self.env = env
async def run(self):
while True:
msg = await self.env.events.get()
print(msg)
# -------- Runner --------
async def main():
env = Environment()
planner = Planner(env)
worker1 = Worker(env, "Worker-A")
worker2 = Worker(env, "Worker-B")
monitor = Monitor(env)
await asyncio.gather(
planner.run(),
worker1.run(),
worker2.run(),
monitor.run()
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Implementing Multiagent systems in Agentic AI
Multiagent systems in Agentic Ai are very dynamic in nature. They have very dynamic environment and agents continuously interact with each other and their environment to achieve the goal. The system requirements, resources and security are the major concerns when designing multiagent system.
- System Requirements – In Multiagent system requirements must be defined. For example what is the final outcome or goal that the system needs to achieve. Nature of environment and how the ai agents will interact with each other and the software tools. Example web scrapping, internet research or handling API calls and similar activities.
- Computational resources – Computational resources can be very high when dealing with multiagent systems because the large language models (llms) are precursor to agentic ai systems. The agents draw the inference and contextual capability from the large language models. Training llms require huge computational resource and powerful hardware resources.
- Security – Cyber security is very important when it comes creating multiagent systems because there is continuous interaction between agents and their environments. Hence implementing robust cyber security for multiagent systems is very important.
How multi agents draw inference from Large language model ?
Large language models (llms) are very good with reasoning and decision making. They have the capability to take human like decisions if trained on right set of datasets which provide them with contextual clarity. Agents draw inference from these llms model which help them perform activity based on decision making capability. This helps ai agents in multi agent agentic environment solve complex problems. It helps autonomous agents to ineract with their environment and take decisions and make actions based on their inference derived from LLMs. A very good example of LLM based multi agents used for software development, society simulation, policy simulation , game simulation etc. It also helps agents to expertise in specific domain and perform task specific to that domain.
- Decision Making process of Agents in Agentic AI environment
- The llm based agents are guided by prompts which are send to large language models. The response from llms are then processed by agents . It then helps the agents to break complex goals/ tasks into smaller sub goals. The agents then take actions on sub goals while learning from past decisions and experiences interacting with llms. It helps them take better decisions on complex world problems.
- Tool usage by AI Agents in multi agents environment
- The agents powered by Large language model have the capability to use the tools and softwares in a dynamic environment. This helps them perform actions and software flow orchestrations. Using this the agents can perform multi steps activity and make them autonomous
- In Context (Memory based learning)
- This ability is derieved from Llm. The in context learning helps agents give them capability to make decisions for solving complex world problems. This gives them human like contextual awarness and decision making capability. It also fascilitates inter agent interactions and collective decision making.
Large Language Based Multi Agents Systems in Agentic AI
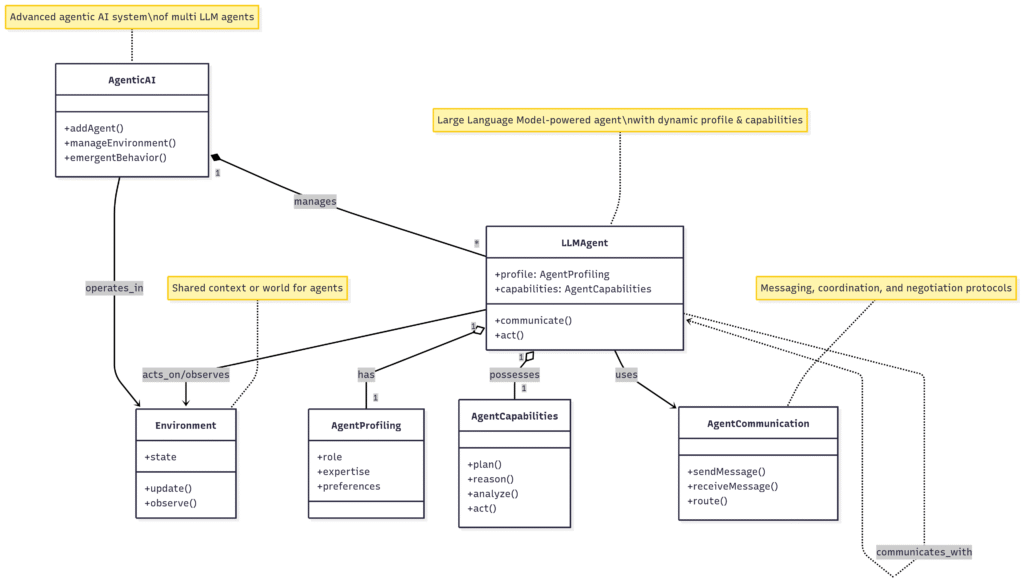
A diagram showing Large Language Based Multi Agents Systems in Agentic AI
-
Environment
- The environment defines the context in which the Multi agent systems are deployed. The environment settings are set based on the final outcome / goal that has to be achieved by agents. The LLM based agents perceive and act within their scope of environment. The environment influences their behavior and decision making.
-
Agents Profiling
- Agent profiling is divided into multiple sub category.
- Pre defined agent profiling – Pre defined agent profiling is defined by system engineers. These profiling are mandatory and are part of system design. So pre defined agent profiling is important in defining the characteristic of an agent.
- Model based agent profiling – This profiling is done based on the model (large language model) we are using for defining agent profile. They inherit model characteristics. Model profiling helps agents get expertise for a specific domain and its related tasks.
- Data derived agent profiling – Data driven agent profiling is done based on pre existing datasets available. Here the agents derive their characteristic based on existing data.
- Agent profiling is divided into multiple sub category.
-
Agents Communication
Agents exchange information in structured ways:
-
-
Direct Messaging:
-
Point-to-point messages (
send → receive). -
Example: Worker reports status back to Planner.
-
-
Broadcast / Pub-Sub:
-
All agents subscribe to a common channel (blackboard, event bus).
-
Example: Monitor listens to all events.
-
-
Negotiation & Coordination:
-
Agents may negotiate for resources, tasks, or roles (contract net protocol).
-
Example: Multiple workers bid for a high-priority task.
-
-
Shared Memory / State:
-
Agents read/write from a central state (database, blackboard).
-
Example: Shared task queue.
-
-
- Agent Capabilities
Each agent type usually has different abilities, e.g.:
-
-
-
Planner Agent
-
Goal decomposition (SMART → subtasks).
-
Dependency management (DAG building).
-
Task assignment & scheduling.
-
-
Worker Agent
-
Executes atomic tasks.
-
Reports progress/outcomes.
-
Can retry, adapt, or escalate failures.
-
-
Monitor Agent
-
Observes environment.
-
Tracks metrics, detects anomalies.
-
Provides feedback loops.
-
-
Negotiator Agent
-
Allocates resources.
-
Resolves conflicts between competing agents.
-
-
Learning Agent
-
Learns from execution logs.
-
Updates strategies, priorities, or models
-
-
-
Agentic AI Use Cases using Multi Agent
Agentic AI use cases are divided into mostly two categories
-
Problem Solving
- Software development
- Agents Environment – Sandbox – Usually when using multi agents in agentic ai systems , agents are used to create sandbox for software development. These sandbox simulate real world environment for software. Sandboxes are very helpful for testing software for real world scenarios.
- Agent Profiling – In Software development , while dealing with multiagents profiling is done mostly based on pre defined scenarios by system designer and pre trained model. System desginer have idea what kind of environment they want to create for testing softwares using sandbox. Eg CTO , Program manager, Engineers
- Feedback mechanism – The feedback process includes environment , agent interaction and learning from that and human input received during testing.
- Software development
-
World Simulation
-
World Simulation
Society
-
Modest Community (25 persons)
Source: [Park et al., 2023]
Sandbox: Yes
Population: Model-generated
Roles: Pharmacy, shopkeeper
Architecture: –
Mechanism: Environment, Agent interaction
Memory: Memory -
Online community (1000 persons)
Source: [Park et al., 2022]
Sandbox: None
Population: Pre-defined, Model-generated
Roles: Camping, fishing
Architecture: –
Mechanism: Agent interaction
Memory: Dynamic Generation
Gaming
-
WereWolf
Source: [Xu et al., 2023b; Xu et al., 2023c]
Sandbox: Sandbox
Population: Pre-defined
Roles: Seer, werewolf, villager
Architecture: Decentralized
Mechanism: Environment, Agent interaction
Memory: Memory
Psychology
-
Human behavior Simulation
Source: [Aher et al., 2023]
Sandbox: Sandbox
Population: Pre-defined
Roles: Humans
Architecture: –
Mechanism: Agent interaction
Memory: Memory
Economy
-
Macroeconomic simulation
Source: [Li et al., 2023e]
Sandbox: None
Population: Pre-defined, Model-generated
Roles: Labor
Architecture: Decentralized
Mechanism: Agent interaction
Memory: Memory -
Information Marketplaces
Source: [Anonymous, 2023]
Sandbox: Sandbox
Population: Pre-defined, Data-derived
Roles: Buyer
Architecture: Decentralized
Mechanism: Environment, Agent interaction
Memory: Memory
Recommender Systems
-
Simulating user behaviors
Source: [Zhang et al., 2023a]
Sandbox: Sandbox
Population: Data-derived
Roles: Users from MovieLens-1M
Architecture: –
Mechanism: Environment
Memory: Memory
-
-
500 + Github projects on Agentic AI
https://github.com/ashishpatel26/500-AI-Agents-Projects
References from scholarly articles
- https://arxiv.org/html/2402.01680v2
- [2505.10468] AI Agents vs. Agentic AI: A Conceptual Taxonomy, Applications and Challenges